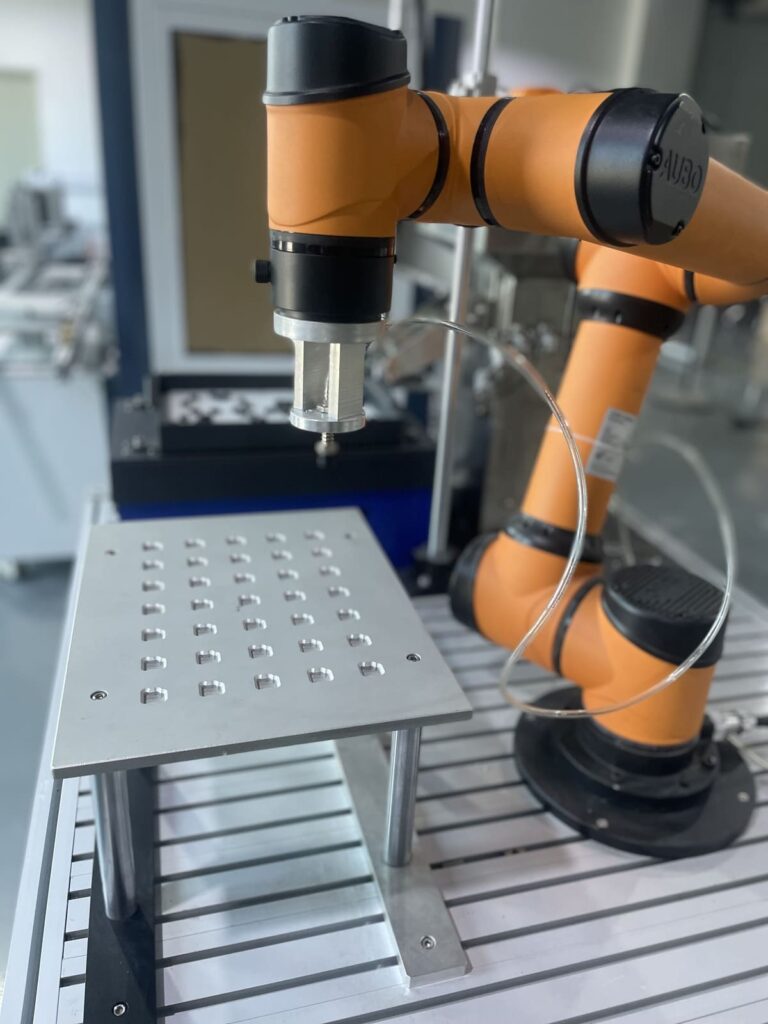
Flexible feeders are a vital component in modern manufacturing facilities, playing a key role in the automation of production lines. These feeders are designed to handle a wide variety of parts and materials, making them versatile solutions for numerous applications.
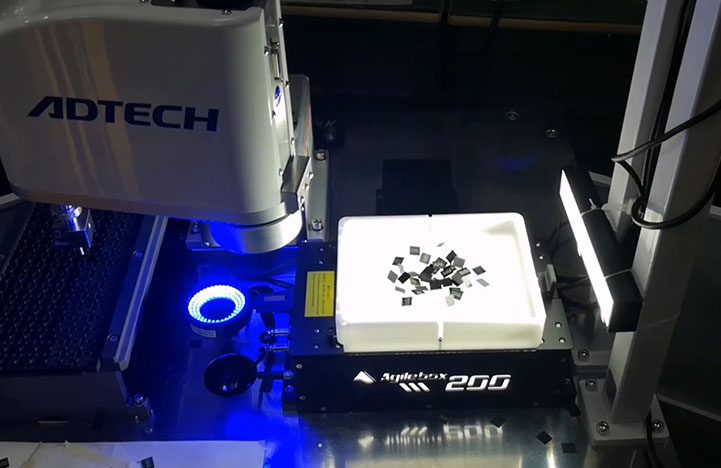

Choosing the right control system for your flexible feeder is crucial to optimize performance, ensuring smooth operation, and maximizing productivity.

manufacturing facilities, playing a key role in the automation of production lines. These feeders are designed to handle a wide variety of parts and materials, making them versatile solutions for numerous applications. Choosing the right control system for your flexible feeder is crucial to optimize performance, ensuring smooth manufacturing facilities, and playing a key role in the automation of production lines.
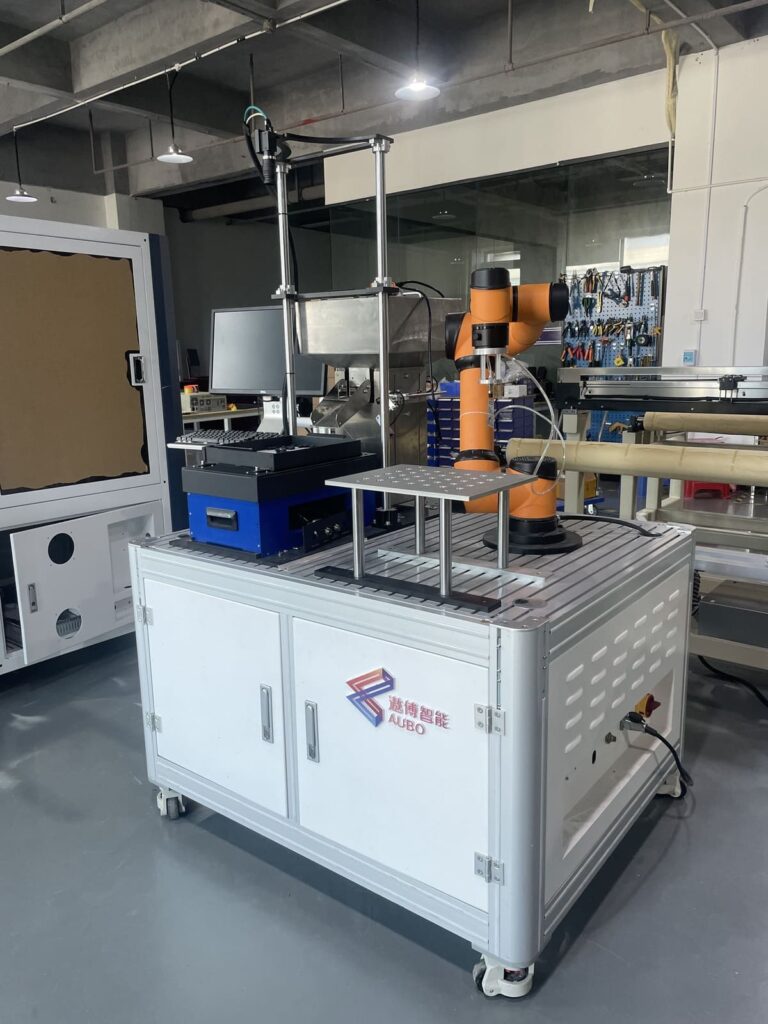

These feeders are designed to handle a wide variety of parts and materials, making them versatile solutions for numerous applications.

Choosing the right control system manufacturing facilities plays a key role in the automation of production lines.

This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of selecting the ideal control system for your flexible feeder, providing valuable insights into factors that should be considered during the decision-making process.

We will also address some frequently asked questions at the end of this article to help clarify any lingering uncertainties.
- Understanding Flexible Feeders
Before diving into the control systems themselves, it’s essential to understand the basics of flexible feeders. These are automated devices designed to orient and present parts to a pick-and-place robot or other handling equipment. Flexible feeders offer several advantages over traditional feeders, such as:

- Adaptability: They can handle a wide variety of parts without needing to change tooling or equipment.
- Scalability: They can accommodate changes in production volume, making them suitable for both low and high-volume applications.
- Efficiency: By enabling quick changeovers and reducing downtime, flexible feeders can significantly improve productivity.
- Key Components of a Flexible Feeder Control System
A control system is the “brain” behind a flexible feeder, responsible for coordinating and managing various subsystems, such as sensors, actuators, and conveyors. The primary components of a flexible feeder control system include:

- Controller: The central processing unit (CPU) responsible for executing control algorithms and managing communication between different subsystems.
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): A device, typically a touchscreen panel, that allows operators to interact with and monitor the control system.
- Input/Output (I/O) Modules: These modules handle communication between the controller and various sensors, actuators, and other devices.
- Communication Protocols: The standardized languages used by control systems to exchange information with external devices, such as PLCs, robots, or other feeders.
- Factors to Consider When Choosing a Control System
To select the right control system for your flexible feeder, it’s important to consider the following factors:

A. Type of Application
The control system you choose should be capable of handling the specific requirements of your application. For example, if your feeder will be used in a high-speed assembly line, you’ll need a control system with fast processing capabilities and the ability to handle complex control algorithms.
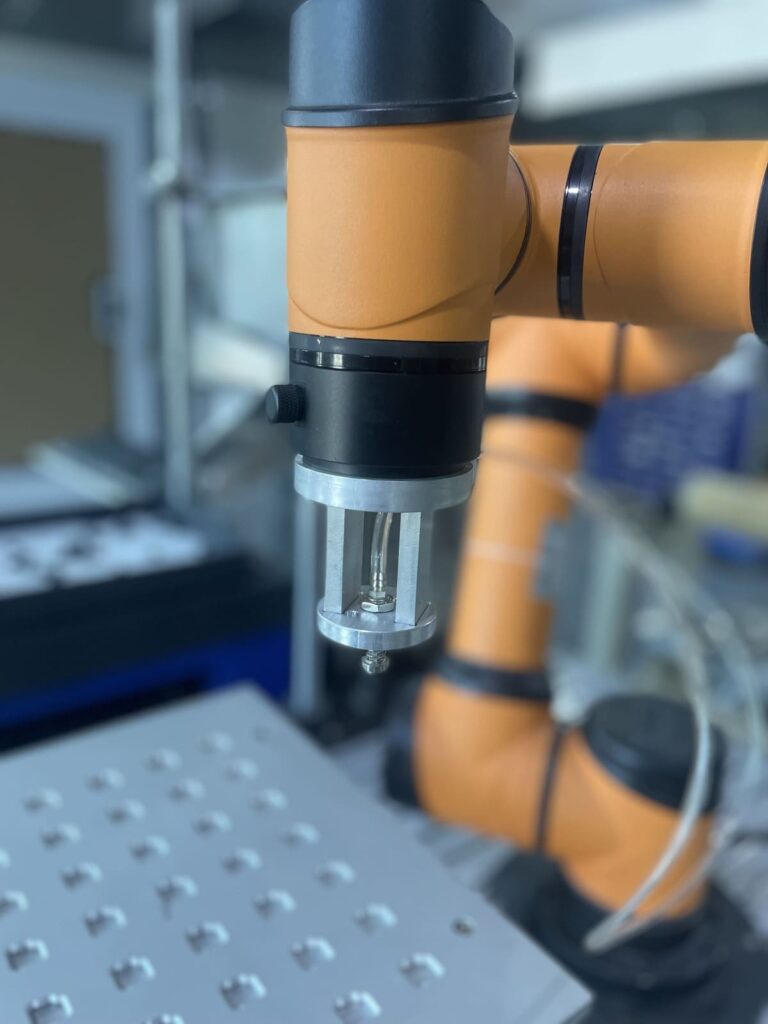

B. Level of Automation
The level of automation in your production environment will directly influence the control system’s requirements. If your facility is highly automated, you’ll need a control system that can seamlessly integrate with other equipment, such as robots, vision systems, and PLCs.
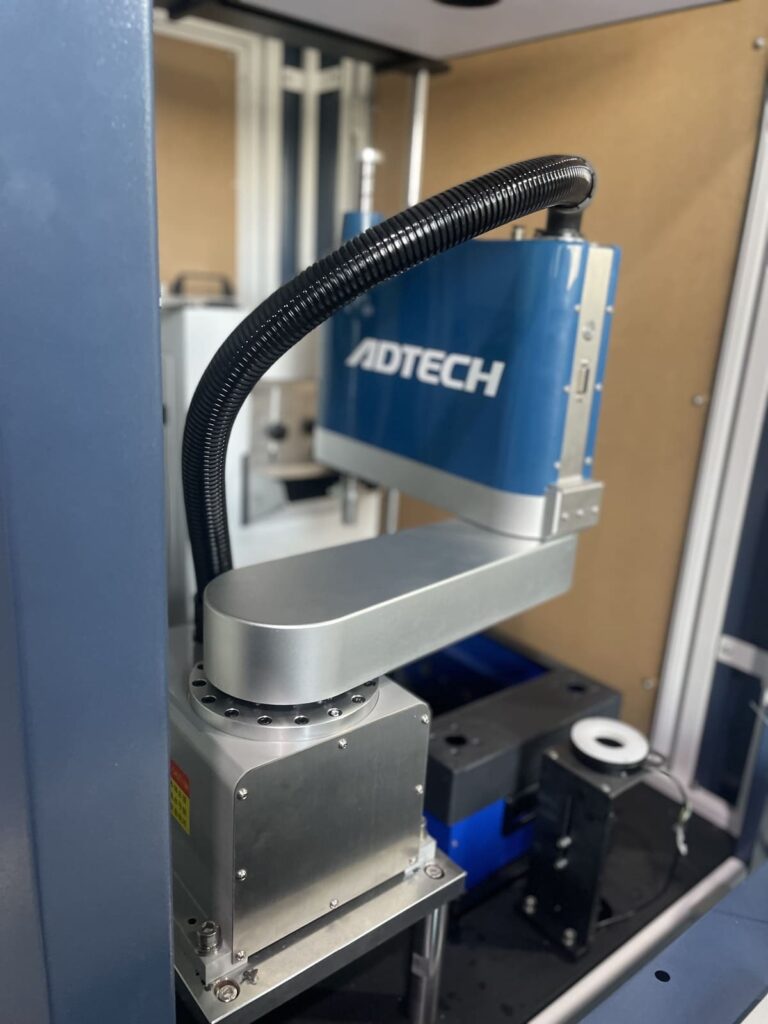

C. Scalability
Your control system should be scalable to accommodate future growth and changes in your production processes. Look for systems that can be easily upgraded or expanded to support new features or increased production demands.
D. Ease of Use
The control system should be user-friendly and easy to operate, with a straightforward HMI interface that allows operators to quickly understand and navigate the system. This will help minimize training time and reduce the risk of errors during operation.

E. Integration with Existing Infrastructure
It’s essential to choose a control system that can easily integrate with your existing production infrastructure, such as PLCs, robots, or conveyor systems. This will help streamline the setup process and reduce overall system complexity.

F. Reliability and Support
Choose a control system from a reputable manufacturer that offers reliable products and ongoing support. This will ensure that you receive prompt assistance in case of any issues or technical difficulties. the manufacturer that offers reliable products and ongoing support.






